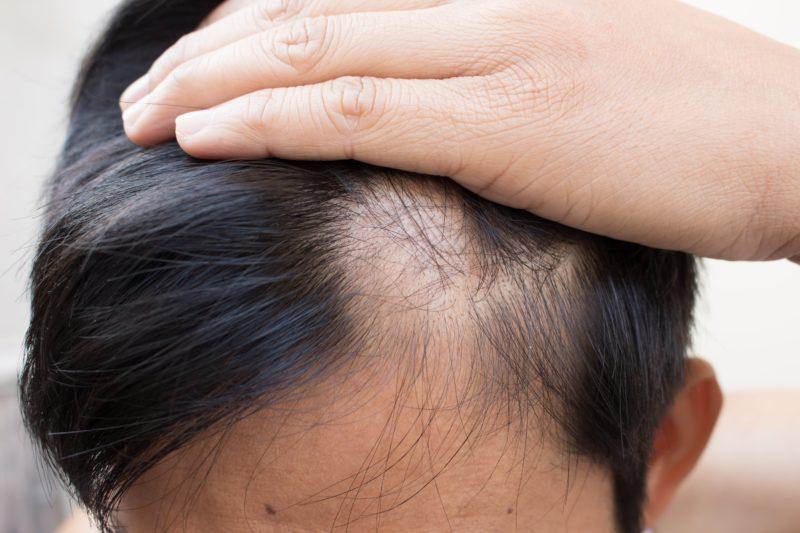

Alopecia means hair loss. One person is a round or oval shaped, without any change in skin, it is a patchy loss of scalp, eyebrow eyelash, beard, mustache or body hair
Why Alopecia areata occurs?
Alopecia areata; autoimmune (a person's own defense cells in the body to see and attack foreign cells) is a disease. Here, alopecia areata develops with defensive cells attacking one's own hair roots.
What are the findings of alopecia areata?
• In the previously bristled areas, one or more coin-sized, rounded, smooth-surface hair loss, other than the loss of patch-like hair loss is seen.
• The hairs in the area or on the edge of the hairs appear narrower at the place where they come out of the skin and resemble an exclamation mark.
• Over time, some patients may lose their hair completely. Therefore, patients with alopecia areata should be followed at the first year when dermatogs are considered suitable.
• In some patients, the hands and toenails can be seen as thin pin (tip). There may also be white spots, fine lines, loss of brightness and breaks. Rarely, the nail may be deformed.
Is Alopecia areata contagious?
Alopecia Areata is not contagious.
Is there genetic transmission of alopecia arta?
People who are genetically predisposed cause a disease with a number of triggering factors.
Can alopecia areata be associated with other diseases?
The risk of alopecia areata is higher in patients with thyroid disease, vitiligo (ala) disease, atopic eczema, and families with asthma, sugar and allergic disease.
How is Alopecia areata diagnosed?
The diagnosis is made by dermoscopic examination or rarely skin biopsy, except for dermatological examination.
How is the treatment of alopecia areata?
• There is no complete treatment of alopecia areata. The bristles can usually come back again in a year. Treatment can help the hairs come back faster.
• In the treatment, the patch-shaped hair loss area may suggest local needles, steroid cream or lotion, oral steroid tablets in common conditions, ditranol cream. One or more of these drugs may be used together.
• Ask your dermatologist about the possible side effects of the medication. Consult your dermatologist as soon as possible for the reactions that occur during your treatment.
When does the disease go?
Most patients recover completely within one year. However, some patients may not respond to treatment. Some may continue to heal and re-shedding.