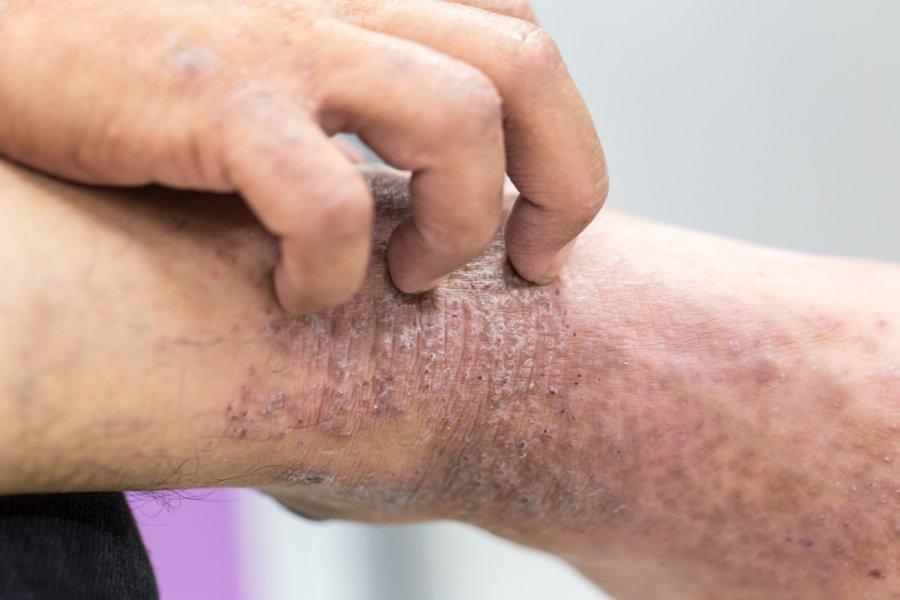

Atopic eczema (dermatitis); is a recurrent skin disease which is more common in young children with skin dryness, rashes and itching, and with occasional exacerbations and improvements. Most atopic eczema individuals have a history of allergic disease, such as allergic asthma and hay fever.
What causes atopic eczema?
The exact cause is not known. It is an extreme reaction of the skin's immune system to environmental and emotional factors. With the deterioration of the protective barrier property of the skin, inflammation and an increased allergic response occur.
Is Atopic Eczema Contagious?
Atopic eczema is not an infectious disease.
Is Atopic Eczema A Genetic Disease?
Atopic eczema is more common in people with atopic eczema, asthma and hay fever. In 1/3 of children with atopic dermatitis, asthma and hay fever may occur later.
What are the symptoms of atopic eczema?
Skin dryness and intense itching are the most important symptoms of the disease. Disturbance of sleep patterns, especially because of itching, fatigue can lead to attention problems in patients' school and work life. Dry, reddened, wholemeal or leaky lesions may occur and recurrent skin rash occurs in different regions and characteristics depending on the age of the patient.
Can atopic eczema symptoms be different in different regions of age?
• In infants and young children, the symptoms usually occur in the face, elbows, or knees, but may also occur in other areas of the body.
• In older children and adults, it usually holds hands, neck, inner face of the elbows, back of knees and ankle.
Can atopic eczema be with other diseases?
• Asthma and hay fever
• Repetitive infections with herpes virus and some bacteria
• Eye problems: Conjunctivitis, cataract
• It may be accompanied by recurrent hand eczema.
How is the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis?
The diagnosis of atopic eczema is based on clinical signs and symptoms. There is no need for any laboratory examination to diagnose atopic eczema.
Are there factors causing the exacerbation of the disease?
It is recommended to stay away from such situations, as the following factors may cause an exacerbation of the disease.
These; increased dryness of the skin (such as long-term and hot bath), scratching, bacteria and viruses caused by infections, emotional stress, sweating, heat and climate changes, cleaners, soaps, detergents, woolen clothes, drapes, dust and plant pollen, smoking, baby and in children, eggs, milk, peanut, soybeans, fish, wheat allergies, contact with animal hair.
What should be considered in the treatment of atopic dermatitis?
Because the disease is chronic and repetitive, the most important step of the treatment is to avoid the exacerbating factors of the disease. Unfortunately, existing treatments do not prevent the occurrence of the disease. For this reason, the best way to take the disease under control is to keep away from the exacerbation factors when your doctor has a good treatment.
What are the medications used in the treatment?
Treatment is determined by the prevalence and severity of the disease. Moisturizers to be used superficially, creams with cortisone, other creams that reduce inflammation, antipruritic drugs, ultraviolet light treatments, defense suppressing drugs can be used.
How do moisturizers work?
Air humidifiers; should be used every day to prevent dryness of the skin. It is better to choose a odorless and colorless product.
How to use drugs with cortisone?
Cortisone creams / ointments; during the active period of eczema control the redness and itching. Your doctor decides where and how long the creams will be used. When cortisone creams are used with moisturizers, the effect is significantly increased and the risk of side effects decreases.
Are there any other creams that reduce fire?
Drugs that contain Tacrolimus and Pimecrolimus in a regional sense reduce redness and inflammation. Do not thinning the skin. Method of use is determined by the dermatologist. The most common side effects are burning and stinging. They can increase the risk of skin infection. Long-term applications should be avoided in the sunshine and they should not be used simultaneously with ultraviolet light therapy.
What are the other treatment methods?
Antipruritic drugs are used in cases where eczema is common, and ultraviolet light treatments are applied in hospital conditions. Drugs that suppress immunosuppression such as azathioprine and cyclosporine may be used in more severe eczema. These treatments have side effects and patients should be monitored by regular blood tests and examination.