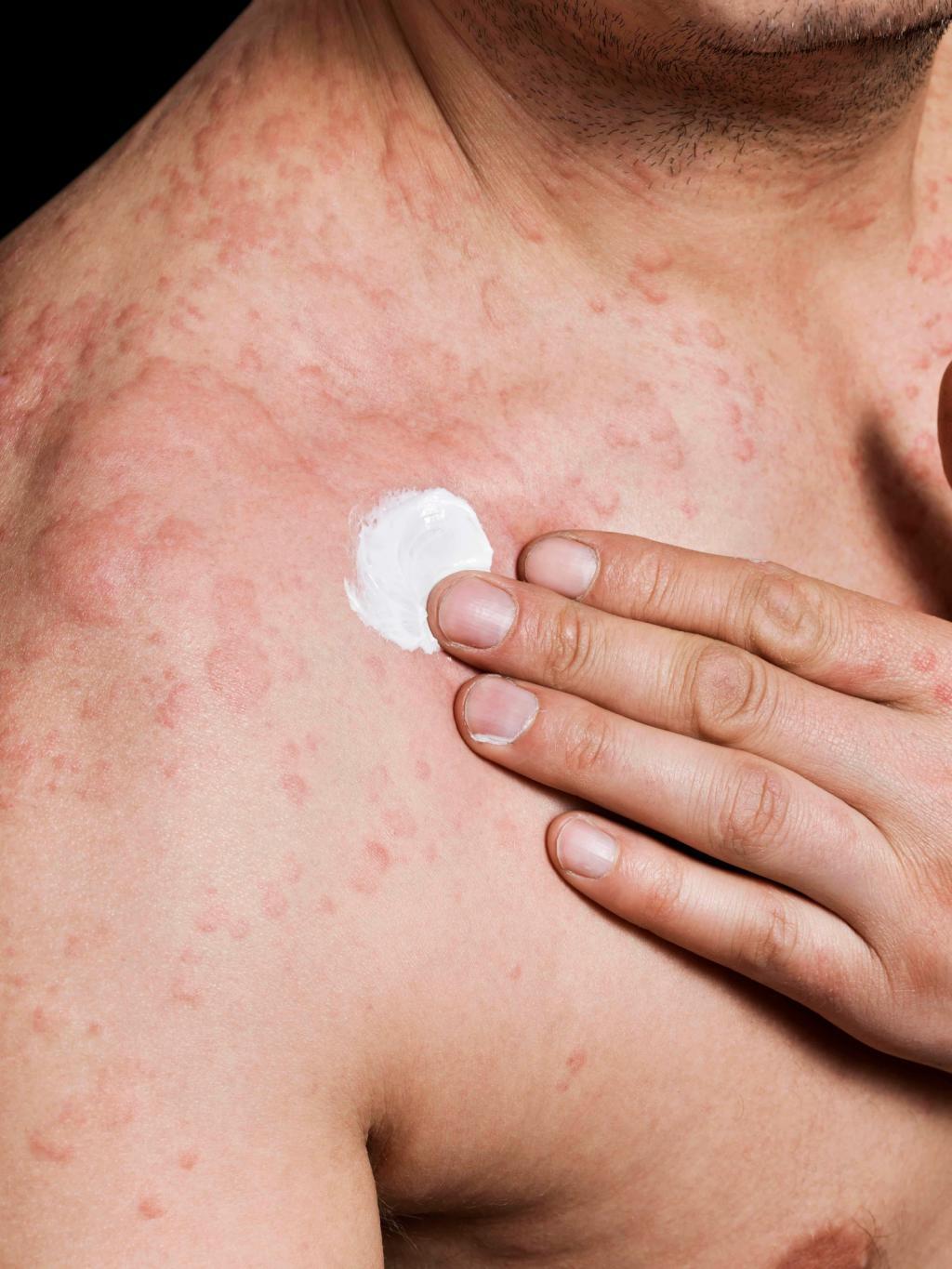

Urticaria (hives) is a common disease characterized by redness, swelling and itching attacks on the skin, which may appear and disappear in a short time.
There are different types of urticaria. The most common form is the usual urticaria. If urticaria attacks are present in the person for less than 6 weeks, ’acute usual urticaria er is called adan chronic usual urticaria‘ if it has been continuing for longer.
What is angioedema?
Angioedema is a form of urticaria, which manifests itself in deeper parts of the skin and gives findings in the form of swelling, swelling, itching or burning-stinging. It is often present in the eyelids, lips and sometimes in the mouth. The hands can be swollen and painful when affected. Ingestion may cause severe symptoms such as dyspnea and difficulty in swallowing. Angioedema and urticaria can be seen separately or together.
What can lead to Urticaria and Angioedema?
In both, the cause of the complaints is the release of histamine from allergy cells in the skin (mast cells). Exercise, pressure on the skin, physical factors such as cold, foods, drugs and infections can stimulate these cells. In some patients with chronic urticaria, their own immune system (autoantibody) structures in the bloodstream of the person stimulate the release of histamine from mast cells in the skin. Normal urticaria usually cannot detect a cause.
What are the findings of Urticaria-Angioedema?
Urticaria is red, itchy, and swellings disappear within 24 hours. These bulges can reach large dimensions as well as they can stay in small dimensions, they can recover from the middle and look like a ring. Angioedema is more common in the eyelids, lips, palms and feet. Sometimes swelling may occur in the mouth and esophagus. This condition causes complaints such as shortness of breath and difficulty in swallowing. Angioedema swelling usually lasts longer than 24 hours.
What factors trigger the disease?
The following factors can trigger the disease:
1. Infections: acute upper respiratory tract infections, especially in the form of flu, flu.
2. Medications: Any drug can cause urticaria, but pain relievers, muscle relaxants and antibiotics are drugs that are more common. Some blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors) may also cause angioedema.
3. Alcohol, food and food additives: foods such as hazelnuts, walnuts, fish, tomatoes and strawberries may be responsible for urticaria.
How is the diagnosis of urticaria?
The findings of the diagnosis of urticaria are diagnostic. In order to find the cause, your doctor will ask you questions and ask for some tests if they deem necessary. Allergy tests have no place in the diagnosis of many types of urticaria.
Are there other types of urticaria other than the usual urticaria?
In some patients, urticaria attacks occur after certain triggers. These triggers are often physical factors (such as pressure, cold, sun exposure), food, drugs, factors that increase body temperature and cause sweating (cholinergic urticaria) and contact with the skin (contact urticaria).
What is the usual treatment of urticaria?
The most important thing in urticaria is to avoid the factors that worsen urticaria.
Drugs used;
• Antihistamines; It is the drugs used primarily in treatment that corrects itching and bulging in many patients. Because they act by preventing the occurrence of discomforting symptoms of the disease, regular use of these drugs on a daily basis (whether or not a bruise) is very important for a successful treatment. Your doctor may increase the dose of your medication when he or she is not able to suppress the disease. Some antihistamines can cause distractions and sleep, while others sleep less, but when taken with alcohol, this group also has drowsiness. For this reason, if you work in jobs that require attention, if you drive and work in jobs where mental activity is required, tell your doctor. Because the duration of the disease may vary from person to person, long-term drug use may be required in some cases.
• In resistant and specific cases, drugs (such as steroids and cyclosporine) that affect the immune system or drugs administered by injection (omalizumab) may be used.
• Tongue and throat swelling is not frequent but angioedema findings. If this is a rare and life-threatening finding, you should consult your nearest health unit.
What can I do to prevent urticaria?
The most important thing is to avoid the factors that increase urticaria. These can be listed as follows:
1. Do not use aspirin (paracetamol is a safe remedy that can be used for this purpose) and aspirin unless very necessary.
2. ACE inhibitors used as hypertension medicines are drugs that should be avoided, especially in patients with angioedema.
3. Do not drink alcohol.
4. Avoid heavy workouts, extreme heat and cold environments.
5. Do not eat foods containing paint and additives.